Every month, Apple’s App Store and Google’s Play Store see thousands of new app submissions—along with a growing list of removals. While most disappear quietly due to inactivity or poor performance, others make headlines. Some of these are hugely popular apps, removed suddenly and without warning, often sparking confusion and debate among users.
These takedowns usually stem from violations of policies around data privacy, security, user safety, or broader legal issues. Here’s a closer look at some of the most notable apps that have been removed by Apple and Google—and why they were pulled from the shelves.
1. Fortnite – Payment Policy Showdown

Fortnite was removed from Apple’s App Store in 2020 when its developer, Epic Games, introduced a direct payment option to bypass Apple’s in-app purchase system. This violated Apple’s strict policy requiring all digital purchases go through its payment gateway, ensuring the company receives a 30% commission.
While Epic took legal action and even won parts of the case in 2024, Apple has continued to block the return of Fortnite in some markets due to lingering policy disputes. As of 2025, Fortnite remains unavailable on iOS devices, despite a large and vocal fan base.
2. Zynn – Plagiarism and Misleading Incentives

Zynn, a TikTok-like short video app, saw rapid growth shortly after its launch but quickly fell under scrutiny. The app was accused of plagiarizing videos from TikTok creators and using an aggressive rewards program that incentivized users to refer friends, raising concerns about manipulative user acquisition tactics.
It was removed from both the App Store and Play Store as regulators and store moderators cracked down on deceptive practices and intellectual property violations.
3. Parler – Content Moderation Failures

Parler, a social media app with a strong emphasis on free speech, was removed from both app stores in early 2021 following the Capitol riots in the U.S. The platform was criticized for failing to moderate violent and extremist content effectively.
Apple and Google determined that the app posed a threat to public safety due to its hands-off moderation policies. While Parler has since made changes and attempted to re-enter the platforms, its popularity has waned considerably.
4. Eitaa Messenger – Sanctions and Geopolitical Pressure

Eitaa, an Iranian messaging app, was taken down from the App Store and Play Store due to broader geopolitical and legal pressures. The app was linked to the Iranian government, and its presence on U.S.-based platforms conflicted with sanctions imposed on certain countries and entities.
Even though it remained popular in its home market, its removal reflected the increasing influence of international politics on app distribution.
5. SpyLoan Apps – Predatory Lending and Data Theft
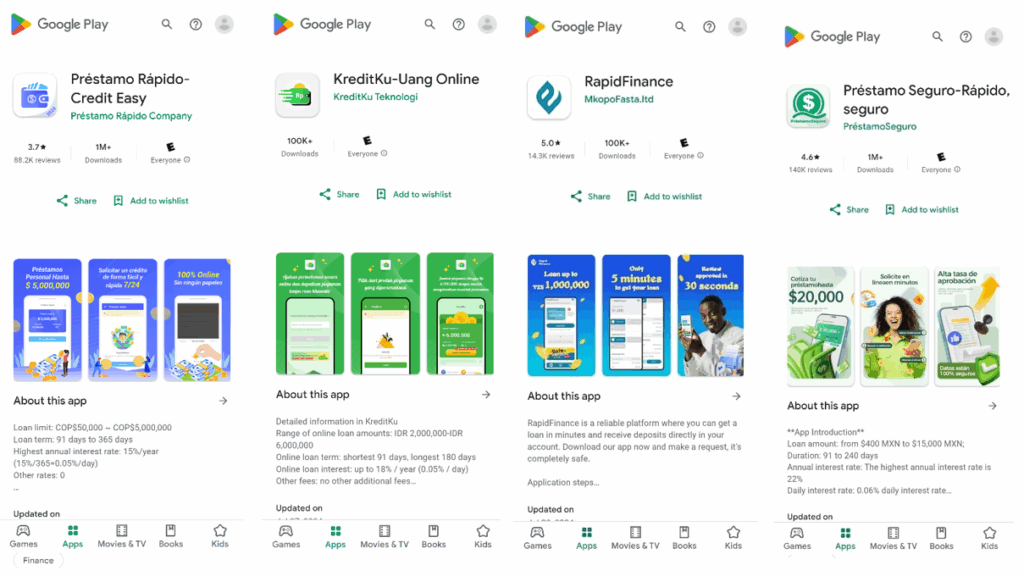
A cluster of apps marketed as instant loan providers—collectively dubbed “SpyLoan” apps—were pulled from Google Play after being found to engage in malicious practices. These apps would offer users quick loans, then collect excessive personal data such as contacts, call logs, and photos.
Victims reported harassment and blackmail if they missed repayment deadlines. Some apps continued to operate through alternative stores or changed their branding, but Google has begun to crack down more heavily on these exploitative platforms.
6. KoSpy Apps – State-Sponsored Surveillance
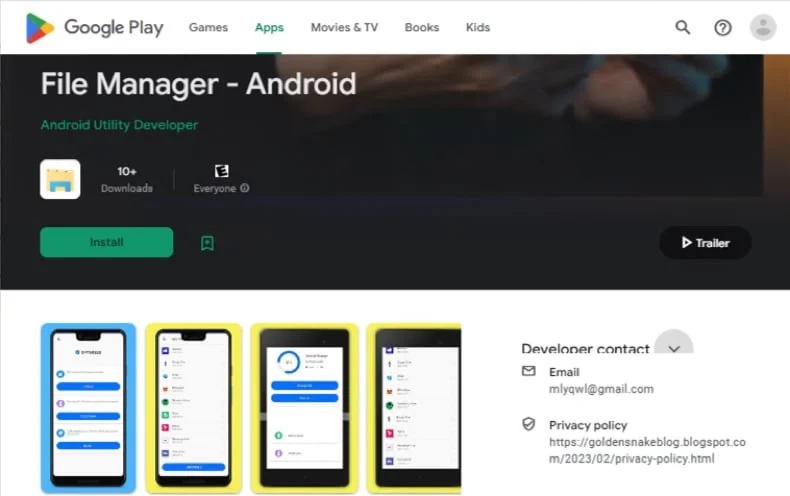
In early 2025, multiple apps were discovered to be part of a surveillance campaign known as KoSpy. Disguised as file managers or utility apps, they covertly collected user data, including messages, location, call history, and even audio recordings.
While the apps appeared harmless on the surface, deeper inspection revealed connections to state-sponsored cyber activity. Google acted swiftly to remove them from the Play Store, though it raised new concerns about how long the apps had been active undetected.
7. AdultSwine Malware – Hidden in Children’s Apps
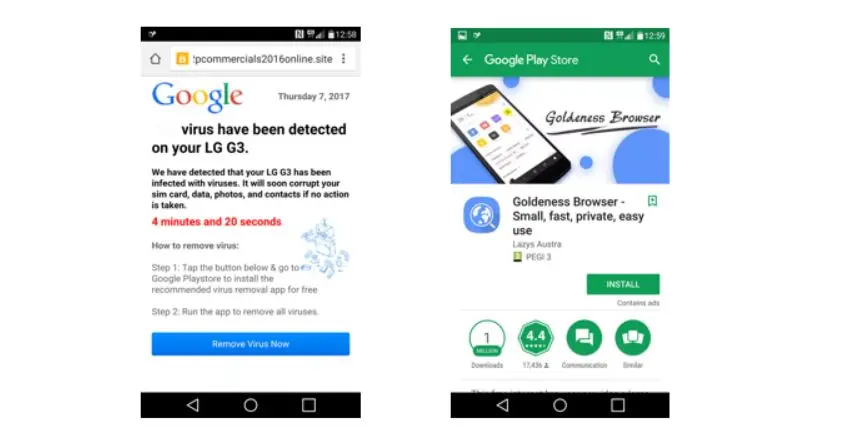
In a particularly disturbing case, dozens of children’s apps were found to contain a malware strain known as AdultSwine. These seemingly innocent apps displayed inappropriate ads, including adult content, and attempted to trick users into downloading more malicious software.
Google removed the apps and banned the developers involved, but the incident highlighted just how vulnerable even child-friendly apps can be to abuse.
8. UC Browser – National Security Concerns

Once one of the most popular mobile browsers in Asia, UC Browser faced bans in several countries due to concerns over data privacy. In India, the app was removed from the Play Store as part of a larger crackdown on Chinese-developed apps that were deemed threats to national security.
Investigations suggested that user data was being transmitted to remote servers without adequate safeguards, prompting swift action by both regulators and platform providers.
9. Signal – Censorship in Authoritarian Markets

Signal, known for its end-to-end encrypted messaging, was removed from the App Store in China. The removal was part of broader internet censorship measures in the country, which increasingly targets foreign apps that promote anonymous communication and privacy.
The move drew criticism from free speech advocates but reflects a growing global trend where governments are exerting more control over what apps are allowed in their regions.
10. Gcam Community, MIUI Downloader – Policy Enforcement Without Warning
Several utility apps with large followings were suddenly delisted from the Play Store, including Gcam Community and MIUI Downloader. Despite millions of downloads and no clear evidence of harm, the apps were removed, leaving users and developers frustrated.
Speculation suggests the removals may have stemmed from unclear policy violations related to data permissions or third-party code, but the lack of transparency in the process has raised concerns within the developer community.
Conclusion
The reasons why apps are removed from the App Store or Google Play vary widely—from serious issues like malware and surveillance to murky policy enforcement and geopolitical factors. For users, these removals are a reminder that popularity does not guarantee safety or longevity.
It also underscores the importance of reading app permissions, staying informed about updates, and relying on reputable sources when downloading new software. As mobile ecosystems become more complex, the line between innovation and regulation continues to be tested—sometimes at the expense of even the most popular apps.