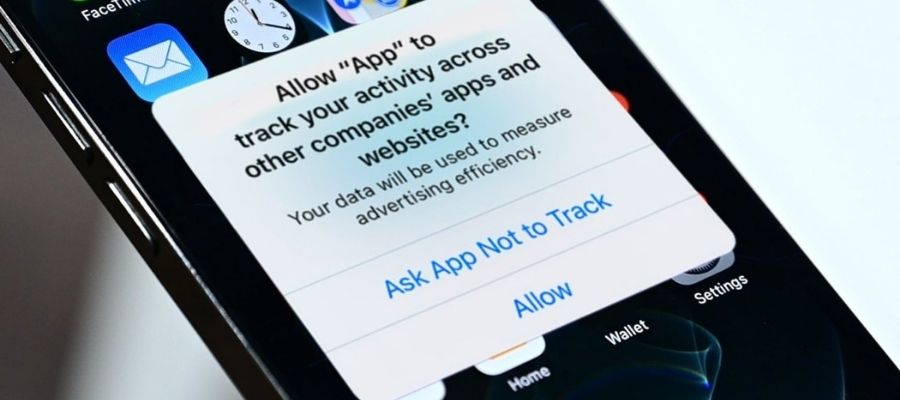
Privacy has become more than just a feature—it’s a necessity. In 2025, the digital landscape continues to shift in response to growing concerns over data collection, tracking, and user consent. Tech giants are under pressure to comply with global privacy regulations while still delivering personalized and seamless user experiences. As a result, the biggest platforms and apps have rolled out substantial updates to align with new expectations around transparency and user control.
Below is a look at the most impactful privacy updates affecting popular apps and platforms this year.
1. Android 16 Introduces Major Privacy Protections

Google’s latest mobile operating system, Android 16, includes sweeping privacy enhancements. The new release introduces an extended version of the Advanced Protection Program, offering high-security settings for users at risk of digital targeting, such as journalists and activists.
One of the standout additions is the Privacy Sandbox, which reduces reliance on invasive tracking techniques by shifting data processing to the device itself. Additionally, Android 16 debuts encrypted intrusion logging, storing device activity securely in the cloud, accessible only to verified security teams. These measures aim to strike a balance between personalization and user control.
2. iOS 17 Reinforces User Autonomy
Apple continues to double down on privacy with iOS 17. The update brings the ability to create separate Safari profiles for work, personal, and school browsing—helping users compartmentalize their digital lives. Private Browsing now requires biometric authentication to reopen tabs, adding another layer of security for sensitive searches.
In addition, Apple’s revamped Private Browsing mode automatically blocks known trackers and removes URLs that might leak user identity. These features solidify Apple’s stance on giving users more control over their online footprint.
3. Pinterest Expands Data Use for AI Training

In a significant policy change, Pinterest now includes provisions to use public user content for training generative AI models. This update applies retroactively, covering content shared on the platform as far back as 2010.
While the company maintains that the data will be anonymized, the move has sparked conversations about transparency and the rights users have over their content. It also exemplifies the broader shift in how platforms leverage user data for machine learning development.
4. Amazon Echo Moves Voice Processing to the Cloud

Amazon has shifted all Alexa voice request processing to its cloud infrastructure. Previously, some voice commands were handled locally on the device for faster response and greater privacy. Now, every command is transmitted and processed remotely, allowing for more sophisticated AI handling but raising new questions about data retention and surveillance.
Users now have to weigh the tradeoff between improved smart assistant functionality and increased reliance on cloud-based data processing.
5. Encrypted Messaging Across Platforms

A long-requested feature is finally becoming reality: Apple plans to support encrypted messaging between iPhones and Android devices using Rich Communication Services (RCS). This will replace unencrypted SMS as the default for cross-platform texts, significantly improving privacy for mixed-device conversations.
With this move, users across both ecosystems can expect secure communication without needing third-party apps like Signal or WhatsApp for basic messaging.
6. Government Requests for Encrypted Data Access

Privacy isn’t just under pressure from companies—governments are stepping in too. In a notable case this year, authorities have demanded that tech firms build back doors into encrypted cloud services. These demands are justified under national security and anti-terrorism laws, but critics argue they risk weakening global encryption standards.
The situation illustrates the ongoing tension between law enforcement needs and the fundamental right to privacy in the digital age.
7. Decentralized Identity Gains Momentum

One of the most transformative trends in 2025 is the shift toward decentralized identity solutions. These frameworks allow users to own and control their personal data directly, instead of entrusting it to central servers. A growing number of apps and platforms now support digital wallets that store identity credentials, eliminating the need to share sensitive data with every new service.
This approach greatly reduces the risks associated with data breaches and offers users a more secure and transparent way to manage their online presence.
8. Zero Trust Architecture Goes Mainstream
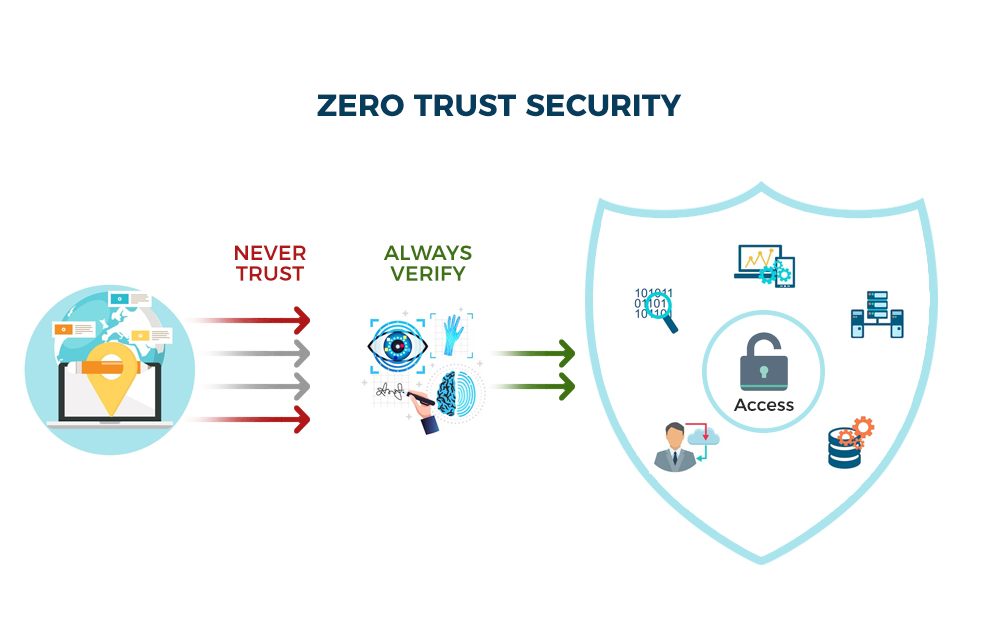
The zero trust model is being widely adopted in enterprise and consumer apps alike. Instead of assuming trust based on network location or credentials, every action must be authenticated and verified continuously.
This model significantly reduces the risk of internal breaches and supports stronger user verification mechanisms across email, cloud services, and productivity tools. As a result, apps that were previously vulnerable to session hijacking or token leaks are now more secure by design.
9. Transparency and Consent Requirements Tighten
Increased global pressure from privacy regulators has forced app developers to be more transparent about how user data is collected, used, and shared. Popular platforms are now required to display simplified, real-time explanations of what data is being collected and for what purpose.
Many apps have introduced dashboard-style settings where users can adjust permissions in detail, revoke consent, and delete their data. This shift is empowering users to make more informed choices about their digital footprints.
10. Privacy by Design Becomes Industry Standard
Privacy by Design is no longer optional—it’s becoming the new baseline. Apps that handle personal data are expected to integrate privacy features at every stage of development, from user onboarding to data storage and processing. This includes default encryption, minimal data collection, and real-time privacy controls.
The result is a new generation of apps that treat privacy as a built-in function rather than a marketing tagline. For users, this means less friction when managing permissions and more confidence in how their information is handled.
Final Thoughts
The privacy landscape in 2025 is evolving faster than ever. From system-level updates in iOS and Android to sweeping policy changes from major platforms like Pinterest and Amazon, users are at the center of a global effort to redefine digital privacy.
While challenges remain—especially when it comes to government access and AI data usage—the momentum is clearly moving toward greater control, transparency, and protection for users. As these updates continue to shape the mobile experience, privacy is no longer a niche concern—it’s a fundamental expectation.